
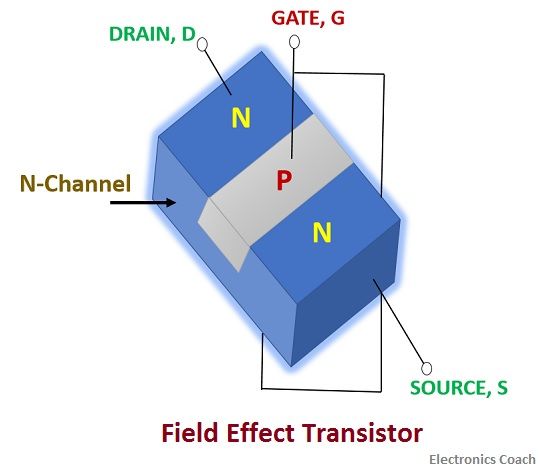
The "metal" in the name MOSFET is sometimes a misnomer, because the gate material can be a layer of polysilicon (polycrystalline silicon). In depletion mode transistors, voltage applied at the gate reduces the conductivity. In an enhancement mode MOSFET, voltage applied to the gate terminal increases the conductivity of the device. The main advantage of a MOSFET is that it requires almost no input current to control the load current, when compared with bipolar transistors (bipolar junction transistors/BJTs). Operating as switches, each of these components can sustain a blocking voltage of 120 V in the off state, and can conduct a continuous current of 30 A in the on state, dissipating up to about 100 W and controlling a load of over 2000 W.

Two power MOSFETs in D2PAK surface-mount packages. The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. The metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor ( MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
